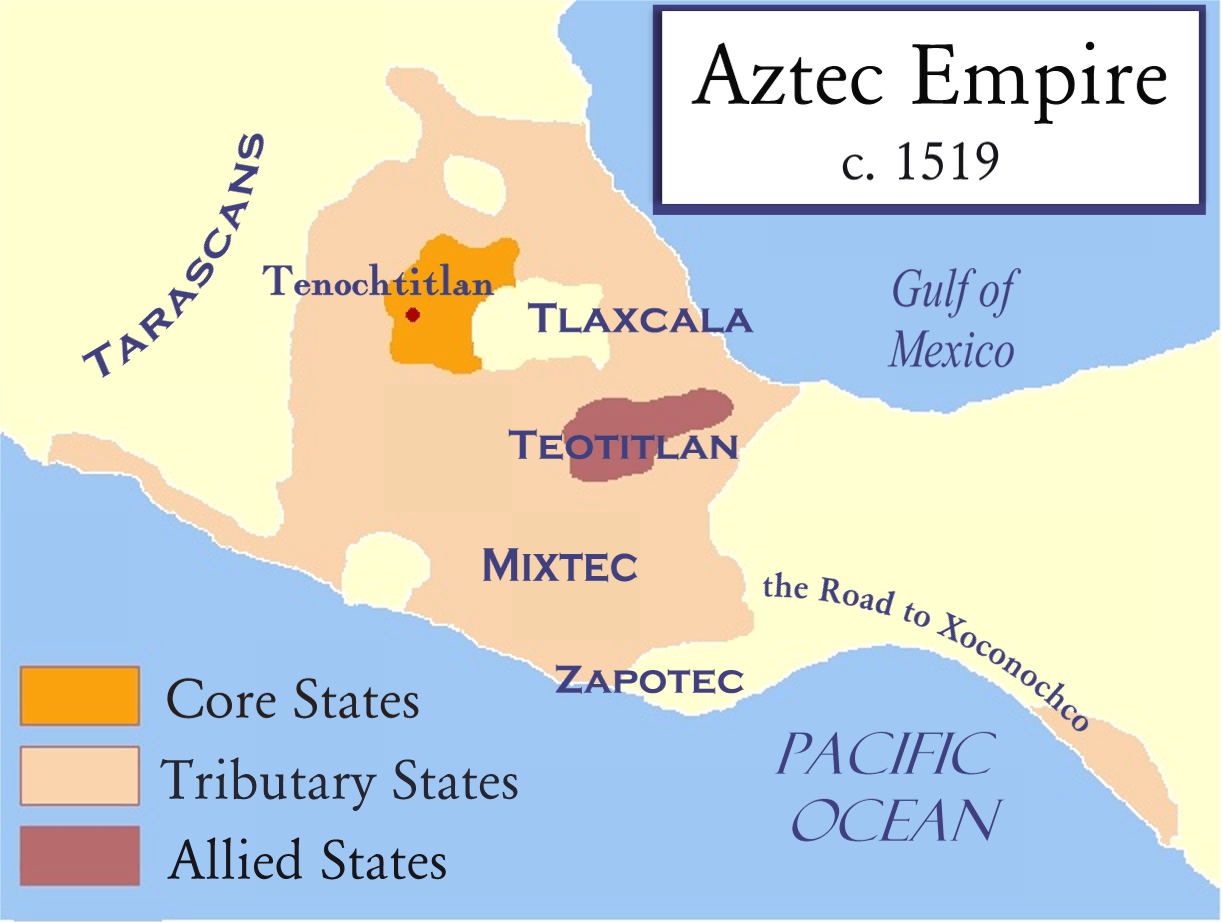
The Aztec Alliance, known as the Triple Alliance, was a significant political and military coalition formed in the early 15th century, consisting of the city-states of Tenochtitlan, Texcoco, and Tlacopan. This alliance played a crucial role in the expansion and consolidation of the Aztec Empire, setting the stage for one of the most powerful civilizations in Mesoamerican history. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the Aztec Alliance, exploring its origins, structure, and the impact it had on the region. We will also examine the socio-political dynamics that allowed this coalition to thrive and dominate its neighbors.
The Aztec Alliance's formation was not merely a result of military necessity but also a strategic response to the socio-political landscape of Mesoamerica at the time. Each city-state brought its strengths and resources to the alliance, creating a formidable force that could challenge other regional powers. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the Aztec Alliance, highlighting its historical significance and the lasting legacy it left behind.
As we explore this topic, we will address the expertise, authority, and trustworthiness of the sources we use, ensuring that the information presented is accurate and reliable. By the end of this article, readers will have a deeper understanding of the Aztec Alliance and its crucial role in shaping the history of Mesoamerica.
Table of Contents
- History of the Aztec Alliance
- Formation of the Triple Alliance
- Structure and Functioning
- Expansion of the Alliance
- Conflicts and Challenges
- Decline of the Aztec Alliance
- Legacy of the Aztec Alliance
- Conclusion
History of the Aztec Alliance
The Aztec Alliance emerged in the early 1400s as a response to the shifting power dynamics in the Valley of Mexico. Prior to the alliance, the region was characterized by fragmented city-states often at war with one another. The need for security and stability prompted the formation of strategic alliances.
The Rise of Tenochtitlan
Tenochtitlan, the capital of the Aztec Empire, was founded in 1325 on an island in Lake Texcoco. Its strategic location allowed it to control trade routes and resources, leading to its rapid growth and influence. The leadership of Tenochtitlan sought to forge alliances with neighboring city-states to enhance its power and security.
Early Alliances
Before the formation of the Triple Alliance, Tenochtitlan had established various alliances, but these were often unstable. The need for a more robust coalition became evident as the city faced threats from rival states like the Tepanecs. This context set the stage for the eventual formation of the Triple Alliance.
Formation of the Triple Alliance
The formal establishment of the Triple Alliance occurred in 1428, when Tenochtitlan, Texcoco, and Tlacopan came together to confront the Tepanec dominance in the region. This coalition was not arbitrary; it was built on mutual interests and the promise of shared resources and military support.
Key Figures in the Alliance
The leaders of the three city-states played a critical role in the formation of the alliance. The most notable among them was Itzcali, the ruler of Tenochtitlan, who was instrumental in negotiating terms and fostering cooperation among the allies.
The Alliance Agreement
The agreement established a framework for mutual defense, resource sharing, and collective military action against external threats. Each city-state retained a degree of autonomy while committing to support one another in times of conflict.
Structure and Functioning
The Triple Alliance operated under a unique structure that facilitated cooperation while preserving the individual identities of each member. The leadership roles were distributed among the three city-states, ensuring that power was not concentrated in one location.
Leadership Dynamics
The leadership of the alliance rotated among the three city-states, with each taking turns in leading military campaigns and making strategic decisions. This system promoted equality and helped to maintain balance among the allies.
Military Organization
The military structure of the alliance was well-organized, with a shared army composed of warriors from all three city-states. This collective military force enabled the alliance to engage in large-scale campaigns against common enemies.
Expansion of the Alliance
Following its formation, the Triple Alliance embarked on a series of military campaigns that significantly expanded its territory and influence throughout Mesoamerica. This period marked the zenith of the Aztec Empire.
Conquest of Neighboring City-States
The alliance systematically conquered neighboring city-states, incorporating them into the growing empire. Notable conquests included the subjugation of the Tepanecs and other rival states, which further solidified the alliance's power.
Economic and Cultural Integration
The expansion of the alliance brought about significant economic benefits, including control over trade routes and resources. Cultural exchange flourished as new territories were integrated into the Aztec Empire, contributing to a rich tapestry of Mesoamerican culture.
Conflicts and Challenges
Internal Strife
While the alliance was built on mutual interests, tensions occasionally arose between the member states. Disagreements over resource allocation and military strategies sometimes threatened the stability of the coalition.
External Threats
The alliance faced significant threats from rival powers, particularly the Tlaxcalans and the Purepechas. These conflicts tested the resilience of the Triple Alliance and required strategic adaptability to maintain dominance.
Decline of the Aztec Alliance
The decline of the Aztec Alliance began in the early 16th century with the arrival of Spanish conquistadors, which ultimately led to the fall of the Aztec Empire. The internal structure and external pressures weakened the coalition.
Spanish Conquest
The Spanish conquest, led by Hernán Cortés, exploited existing rivalries within the empire. The alliances that had been built over decades were undermined, leading to a swift collapse of Aztec power.
Impact of European Colonization
The arrival of Europeans not only brought military defeat but also introduced diseases that decimated the indigenous population. This dramatic shift marked the end of the Aztec Alliance and the beginning of colonial rule in Mexico.
Legacy of the Aztec Alliance
The legacy of the Aztec Alliance is profound, influencing the culture, politics, and social structures of subsequent civilizations in Mesoamerica. Its impact can still be felt today.
Cultural Influence
The cultural achievements of the Aztec Empire, such as art, architecture, and religious practices, were significantly shaped by the alliance. The integration of diverse cultures enriched Mesoamerican heritage.
Historical Significance
The Aztec Alliance serves as a case study for understanding the complexities of power dynamics in ancient civilizations. Its rise and fall offer valuable lessons on the importance of cooperation and the challenges of maintaining alliances in a competitive environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Aztec Alliance was a pivotal force in shaping the history of Mesoamerica. Through its strategic formation, military expansion, and eventual decline, it illustrates the complexities of political alliances and the impact of external forces on indigenous civilizations. As we reflect on the legacy of the Aztec Alliance, we invite readers to engage with this rich history, share their thoughts in the comments, and explore further articles on related topics.
The story of the Aztec Alliance is not just a chapter in history; it is a testament to human resilience and the intricate web of relationships that define our past. Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you back on our site for more insightful articles!
Exploring The Life And Career Of Johnny Ramistella
Jack Antonoff: The Musical Visionary Behind 6:16
Sweeping Bob: The Ultimate Guide To Mastering This Iconic Hairstyle